


Chapter 6
I Construction During The Settlement Years
II The Use Of Timber As A Structural Material
III Structural Steel
IV Concrete Technology
V Housing
VI Industrialised Pre-cast Concrete Housing
VII Ports And Harbours
VIII Roads
IX Heavy Foundations
X Bridges
XI Sewerage
XII Water Engineering
XIII Railways
XIV Major Buildings
XV Airports
XVI Thermal Power Stations
XVII Materials Handling
XVIII Oil Industry
i All Welded Storage Tanks
ii Insulated Fuel Oil Pipeline
iii Wartime Concrete Tanks
iv The Cobia 2 Sub-sea Completion
v Mackerel and Tuna Platforms
vi Snapper Post-Trenching Plough
vii The North West Shelf Project Plough
XIX The Snowy Mountains Scheme
XX The Sydney Opera House
XXI The Sydney Harbour Bridge
XXII Hamersley Iron
XXIII North West Shelf
Sources and References
Index
Search
Help
Contact us

The Cobia 2 Sub-sea Completion
Sub-sea completions are recognised world-wide as a cost effective means of developing marginal reservoirs, accelerating production and draining reservoir extremities which cannot be reached from conventional platforms. To date, more than 280 sub-sea completions have been installed around the world. Cobia 2, the first sub-sea completion in Australian waters, began production in Bass Strait in June 1979 (Fig. 72). Both the Cobia 2 and the Mackerel A-14 wells are considered to be significant achievements. The Mackerel A-14 achieved a combination of extremely high angle, together with deep true vertical depth drilling. While other wells may have been drilled to higher deviation none, to our knowledge, has been drilled to the depth that was attained by the well drilled from the Mackerel 'A' platform. The Cobia-2 well represents a completion which is also at the forefront of technology, primarily because of the use of the electro-hydraulic control system, plus the length of flowline used.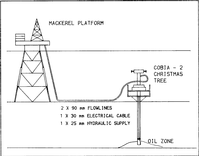
People in Bright Sparcs - Gorrie, A. W.
 |
Australian Academy of Technological Sciences and Engineering |  |
© 1988 Print Edition page 417, Online Edition 2000
Published by Australian Science and Technology Heritage Centre, using the Web Academic Resource Publisher
http://www.austehc.unimelb.edu.au/tia/418.html